Arduino Interface LED
This article is a continuation of the series on “Arduino Interface – LED” and carries the discussion on Turn ON/OFF, and blinking of LED in the Arduino Environment.
- LED (light-emitting diode): LED is a simple diode that emits light in a forward bias
- Arduino: is an open-source, board that has a Microchip ATmega328P microcontroller on it.
Pre-Request
- PC
- Arduino IDE setup or web-based IDE
Components Required
- LED – 1 Nos,
- Resistor, 220 Ohm – 1Nos
- Breadboard (Optional: If required)
- Arduino UNO
- Jumper wires
Turn On/Off LED
The program simply turns ON and OFF LED with some delay between them.
- For Turn OFF LED – Set digital pin Low
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW); - For Turn ON LED – Set digital pin high
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH);

LED Blink
ED blinking is a common demonstration in electronics and microcontroller-based projects. It refers to the process of turning a Light Emitting Diode (LED) on and off in a repetitive pattern

Blinking LED circuits can be used for signaling purposes, such as:
- A signal for help
- A flashing beacon
- A vehicle indicator when it is broke down
Blinking LED circuits use electronic oscillators and digital timing to provide visual alerts and indications.
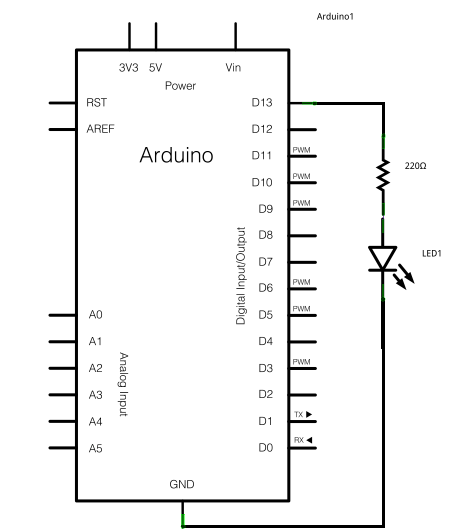
Circuit
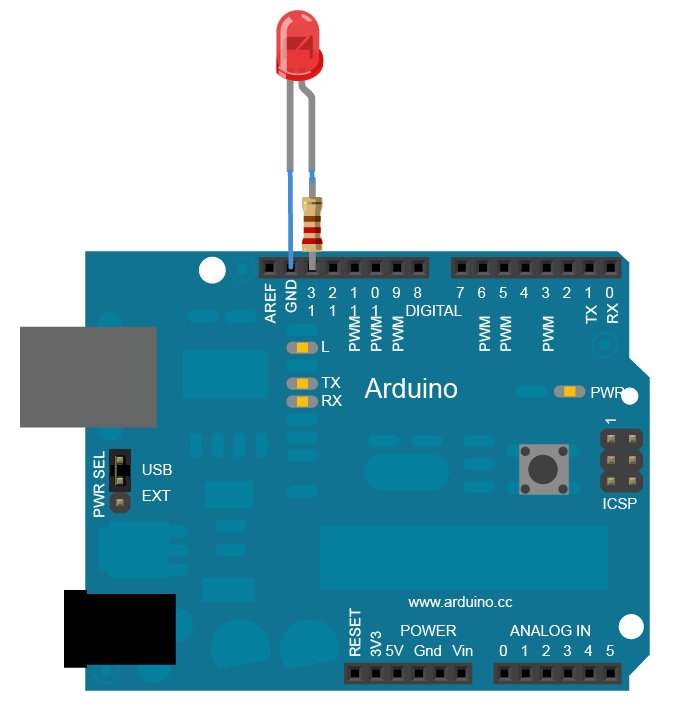
Schematic
Code: Blink LED using Delay Function in the loop
/*
Blink
Turns on an LED on for one second, then off for one second, repeatedly.
This example code is in the public domain.
*/
// Pin 13 has an LED connected on most Arduino boards.
// give it a name:
int led = 13;
// the setup routine runs once when you press reset:
void setup() {
// initialize the digital pin as an output.
pinMode(led, OUTPUT);
}
// the loop routine runs over and over again forever:
void loop() {
digitalWrite(led, HIGH); // turn the LED on (HIGH is the voltage level)
delay(1000); // wait for a second
digitalWrite(led, LOW); // turn the LED off by making the voltage LOW
delay(1000); // wait for a second
}
Code: Blink Without Delay function in loop
/*
Blink without Delay
Turns on and off a light emitting diode (LED) connected to a digital pin,
without using the delay() function. This means that other code can run at the
same time without being interrupted by the LED code.
The circuit:
- Use the onboard LED.
- Note: Most Arduinos have an on-board LED you can control. On the UNO, MEGA
and ZERO it is attached to digital pin 13, on MKR1000 on pin 6. LED_BUILTIN
is set to the correct LED pin independent of which board is used.
If you want to know what pin the on-board LED is connected to on your
Arduino model, check the Technical Specs of your board at:
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Products
created 2005
by David A. Mellis
modified 8 Feb 2010
by Paul Stoffregen
modified 11 Nov 2013
by Scott Fitzgerald
modified 9 Jan 2017
by Arturo Guadalupi
This example code is in the public domain.
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/BlinkWithoutDelay
*/
// constants won't change. Used here to set a pin number:
const int ledPin = LED_BUILTIN;// the number of the LED pin
// Variables will change:
int ledState = LOW; // ledState used to set the LED
// Generally, you should use "unsigned long" for variables that hold time
// The value will quickly become too large for an int to store
unsigned long previousMillis = 0; // will store last time LED was updated
// constants won't change:
const long interval = 1000; // interval at which to blink (milliseconds)
void setup() {
// set the digital pin as output:
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// here is where you'd put code that needs to be running all the time.
// check to see if it's time to blink the LED; that is, if the difference
// between the current time and last time you blinked the LED is bigger than
// the interval at which you want to blink the LED.
unsigned long currentMillis = millis();
if (currentMillis - previousMillis >= interval) {
// save the last time you blinked the LED
previousMillis = currentMillis;
// if the LED is off turn it on and vice-versa:
if (ledState == LOW) {
ledState = HIGH;
} else {
ledState = LOW;
}
// set the LED with the ledState of the variable:
digitalWrite(ledPin, ledState);
}
}
LED Fade
LED fading refers to the gradual change in brightness of an LED (Light Emitting Diode). This effect is often used in lighting projects to create smooth transitions between different light intensities, giving a more visually appealing and dynamic result. Fading can be achieved through various methods, and one common approach is to use Pulse Width Modulation (PWM).
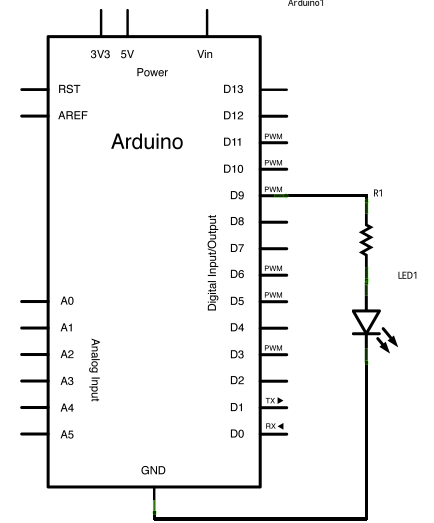
Circuit
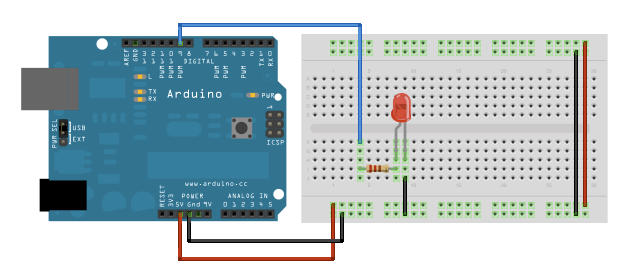
Schematic
Code
/*
Fade
This example shows how to fade an LED on pin 9 using the analogWrite()
function.
The analogWrite() function uses PWM, so if you want to change the pin you're
using, be sure to use another PWM capable pin. On most Arduino, the PWM pins
are identified with a "~" sign, like ~3, ~5, ~6, ~9, ~10 and ~11.
This example code is in the public domain.
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/Fade
*/
int led = 9; // the PWM pin the LED is attached to
int brightness = 0; // how bright the LED is
int fadeAmount = 5; // how many points to fade the LED by
// the setup routine runs once when you press reset:
void setup() {
// declare pin 9 to be an output:
pinMode(led, OUTPUT);
}
// the loop routine runs over and over again forever:
void loop() {
// set the brightness of pin 9:
analogWrite(led, brightness);
// change the brightness for next time through the loop:
brightness = brightness + fadeAmount;
// reverse the direction of the fading at the ends of the fade:
if (brightness <= 0 || brightness >= 255) {
fadeAmount = -fadeAmount;
}
// wait for 30 milliseconds to see the dimming effect
delay(30);
}
Arduino Interface – LED ON/OFF Using Single Button
Schematics
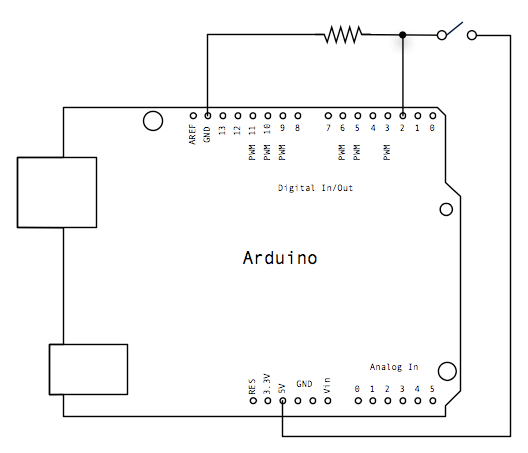
Code
/*
Button
Turns on and off a light emitting diode(LED) connected to digital pin 13,
when pressing a pushbutton attached to pin 2.
The circuit:
- LED attached from pin 13 to ground
- pushbutton attached to pin 2 from +5V
- 10K resistor attached to pin 2 from ground
- Note: on most Arduinos there is already an LED on the board
attached to pin 13.
created 2005
by DojoDave <http://www.0j0.org>
modified 30 Aug 2011
by Tom Igoe
This example code is in the public domain.
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/Button
*/
// constants won't change. They're used here to set pin numbers:
const int buttonPin = 2; // the number of the pushbutton pin
const int ledPin = 13; // the number of the LED pin
// variables will change:
int buttonState = 0; // variable for reading the pushbutton status
void setup() {
// initialize the LED pin as an output:
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
// initialize the pushbutton pin as an input:
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
// read the state of the pushbutton value:
buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin);
// check if the pushbutton is pressed. If it is, the buttonState is HIGH:
if (buttonState == HIGH) {
// turn LED on:
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
} else {
// turn LED off:
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
}
}
NEXT: