ESP32 Mongoose OS Basic Examples
This article is about ESP32 Mongoose OS – Basic Examples, Let’s go through a basic example of using UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter), Button and blinking an LED using an ESP32 by Mongoose OS.
Mongoose OS is an open-source IoT operating system designed for low-power, connected microcontrollers. Below is a basic example to get you started with Mongoose OS on an ESP32. This example demonstrates how to create a simple firmware that blinks an LED.
This is a basic example to help you get started with Mongoose OS on an ESP32. It blinks an LED using the GPIO capabilities provided by Mongoose OS. From here, you can explore additional features and libraries provided by Mongoose OS to build more sophisticated IoT applications. Refer to the Mongoose OS documentation for detailed information and advanced usage.
Setup Required
- PC
- UART Terminal (Putty, Visual Studio Serial Terminal, DockLight)
- LEDs
UART Serial
Print words, string, text, symbols
print('------------****************----------------');
print('ArunEworld');
ESP32 Mongoose OS – Basic Examples of UART Communication
// https://github.com/cesanta/mongoose-os/blob/master/fw/examples/mjs_uart/init.js
// Load Mongoose OS API
load('api_timer.js');
load('api_uart.js');
load('api_sys.js');
// Uart number used for this example
let uartNo = 1;
// Accumulated Rx data, will be echoed back to Tx
let rxAcc = "";
let value = false;
// Configure UART at 115200 baud
UART.setConfig(uartNo, {
baudRate: 115200,
esp32: {
gpio: {
rx: 16,
tx: 17,
},
},
});
// Set dispatcher callback, it will be called whenver new Rx data or space in
// the Tx buffer becomes available
UART.setDispatcher(uartNo, function(uartNo, ud) {
let ra = UART.readAvail(uartNo);
if (ra > 0) {
// Received new data: print it immediately to the console, and also
// accumulate in the "rxAcc" variable which will be echoed back to UART later
let data = UART.read(uartNo);
print("Received UART data:", data);
rxAcc += data;
}
}, null);
// Enable Rx
UART.setRxEnabled(uartNo, true);
// Send UART data every second
Timer.set(1000 /* milliseconds */, true /* repeat */, function() {
value = !value;
UART.write(
uartNo,
"Hello UART! "
+ (value ? 'Tick' : 'Tock')
+ " uptime: " + JSON.stringify(Sys.uptime())
+ " RAM: " + JSON.stringify(Sys.free_ram())
+ (rxAcc.length > 0 ? (" Rx: " + rxAcc) : "")
+ "\n"
);
rxAcc = "";
}, null);
GPIO Module
- View On GitHub : api_gpio.js
Button (GPIO as Output)
Print the message using Press Button
- First, set the button ‘0’ as the pin variable,
- Set GPIO pin ‘0’ mode as button handler mode with pull up, end negative.
// Load Mongoose OS API
load('api_gpio.js');
let pin = 0; // GPIO 0 is typically a 'Flash' button
GPIO.set_button_handler(pin, GPIO.PULL_UP, GPIO.INT_EDGE_NEG, 200, function(x)
{
print('Button press, pin: ', x);
}, true);
print('www.ArunEworld.com', pin);
print('Flash button is configured on GPIO pin ', pin);
print('Press the flash button now!');
LED Blink using Button
ESP32 Mongoose OS – Basic Examples Code
// Load Mongoose OS API
load('api_gpio.js');
// Configure LED
let led = 23;// ffi('int get_led_gpio_pin()')(); // Get built-in LED GPIO pin
GPIO.set_mode(led, GPIO.MODE_OUTPUT);
let pin = 0; // GPIO 0 is typically a 'Flash' button
GPIO.set_button_handler(pin, GPIO.PULL_UP, GPIO.INT_EDGE_NEG, 200, function(x) {
let value = GPIO.toggle(led);
print('Button press, pin:', x, 'LED pin:', led, ' Value: ', value);
}, true);
print('Flash button is configured on GPIO pin ', pin);
print('Press the flash button now!');
Result
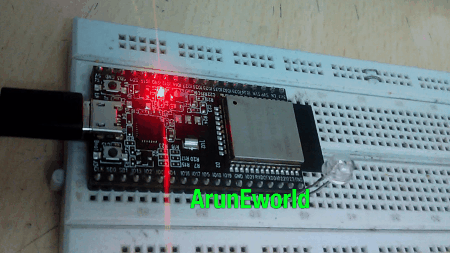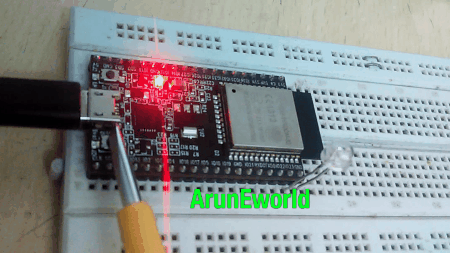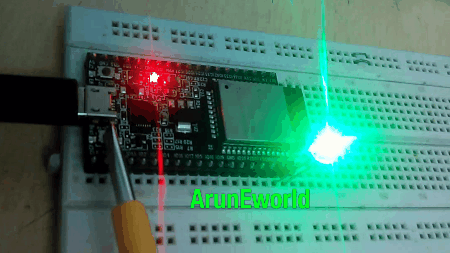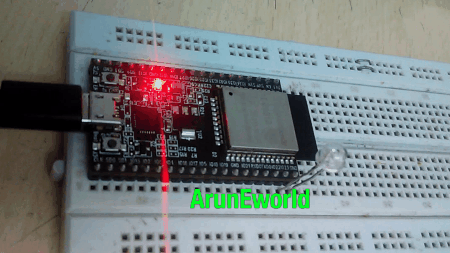
LED Blink Using Timer
// http://www.ArunEworld.com/Embedded/Espresif/ESP32/
// Tested By : Arun(20170430)
// Example Name : AEW_Button_Message.js
// Firmware : Mongoose OS for ESP32
//*******************************//
// Load Mongoose OS API
load('api_timer.js');
load('api_gpio.js');
// Blink 23rd pin LED every second
let PIN = 23;
GPIO.set_mode(PIN, GPIO.MODE_OUTPUT);
Timer.set(1000 /* milliseconds */, true /* repeat */, function(pin) {
let value = GPIO.toggle(pin);
print(value ? 'Tick' : 'Tock');
}, PIN);
ESP32 Mongoose OS – Basic Examples of Button Message
Using buttons in embedded systems is a common practice for user interaction. Buttons, also known as push buttons or tactile switches, are simple input devices that can be used to trigger specific actions or responses within an embedded system. Her example of When button released, Print the values “Tick”& “Tock”.
// https://aruneworld.com/
// Tested By : Arun(20170430)
// Example Name : AEW_LED-Blink.js
// Firmware : Mongoose OS for ESP32
//© 2017 ArunEworld, Inc. Terms
//*******************************//
// Load Mongoose OS API
load('api_timer.js');
load('api_gpio.js');
// Blink 26th pin LED every second
let PIN = 26;
GPIO.set_mode(PIN, GPIO.MODE_OUTPUT);
Timer.set(1000 /* milliseconds */, true /* repeat */, function(pin) {
let value = GPIO.toggle(pin);
print(value ? 'Tick' : 'Tock');
}, PIN);
NEXT
| Mongoose OS |
| |
| ESP32 Mongoose OS Basic Ex |
| ESP32 MongooseOS Interface WiFi |
| ESP32 MongooseOS Interface MQTT |
| |
| ESP32 Mongoose OS All Post |